Istio is a service mesh which provides a dedicated infrastructure layer that you can add to your applications. It adds capabilities like observability, traffic management, and security, without adding them to your own code.
To populate its own service registry, Istio connects to a service discovery system. For example, if you’ve installed Istio on a Kubernetes cluster, then Istio automatically detects the services and endpoints in that cluster. Using this service registry, the Envoy proxies can then direct traffic to the relevant services.
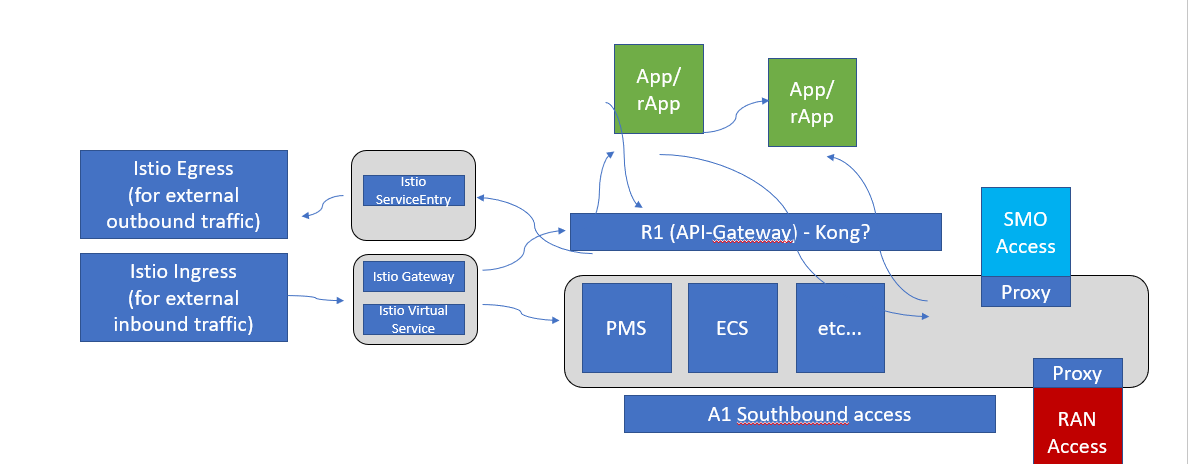
Istio Ingress Gateway can be used as a API-Gateway to securely expose the APIs of your micro services. It can be easily configured to provide access control for the APIs i.e. allowing you to apply policies defining who can access the APIs, what operations they are allowed to perform and much more conditions.
The Istio API traffic management features available are: Virtual services: Configure request routing to services within the service mesh. Each virtual service can contain a series of routing rules, that are evaluated in order. Destination rules: Configures the destination of routing rules within a virtual service.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ratings
spec:
host: ratings.prod.svc.cluster.local
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: LEAST_CONN
subsets:
- name: testversion
labels:
version: v3
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: ROUND_ROBIN |
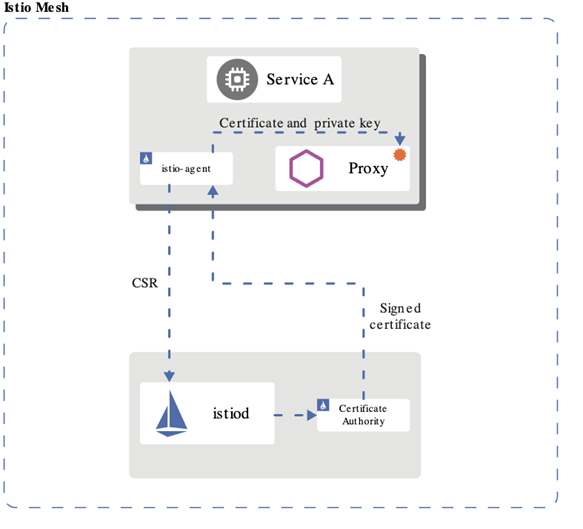
Istio provisions the DNS names and secret names for the DNS certificates based on configuration you provide. The DNS certificates provisioned are signed by the Kubernetes CA and stored in the secrets following your configuration. Istio also manages the lifecycle of the DNS certificates, including their rotations and regenerations.
With Mutual TLS (mTLS) the client and server both verify each other’s certificates and use them to encrypt traffic using TLS.. With Istio, you can enforce mutual TLS automatically.
apiVersion: "security.istio.io/v1beta1"
kind: "PeerAuthentication"
metadata:
name: "default"
namespace: "istio-system"
spec:
mtls:
mode: STRICT |

JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object.
JWT is mostly used for Authorization. Once the user is logged in, each subsequent request will include the JWT, allowing the user to access routes, services, and resources that are permitted with that token (User context). You can pass the original jwt as an embedded jwt or pass original jwt in the http header (Istio / JWTRule).
JWT can also contain information about the client that sent the request (client context).
We can use Istio's RequestAuthentication resource to configure JWT policies for your services.
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: RequestAuthentication
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: foo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: httpbin
jwtRules:
- issuer: "issuer-foo"
jwksUri: https://example.com/.well-known/jwks.json
---
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: foo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: httpbin
rules:
- from:
- source:
requestPrincipals: ["*"] |
JWT can also be used for service level authorization (SLA)
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: foo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: httpbin
rules:
- from:
- source:
requestPrincipals: ["*"]
- to:
- operation:
paths: ["/healthz"] |

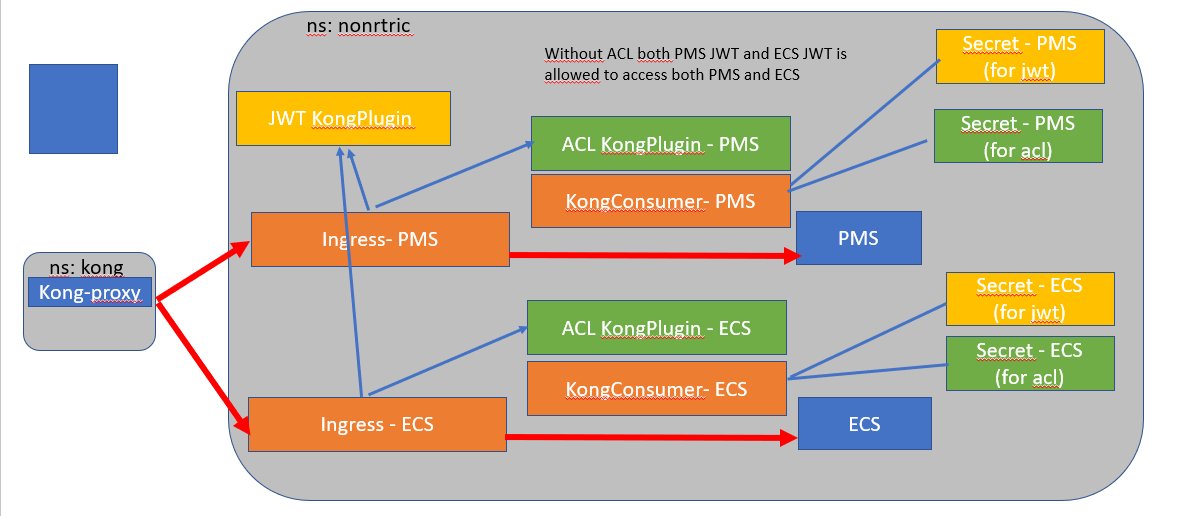
K8S RBAC (Role Based Access Control) - supported by default in kubernetes.
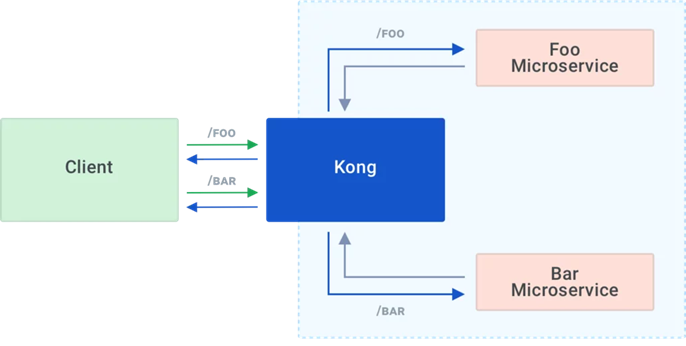
Kong is Orchestration Microservice API Gateway. Kong provides a flexible abstraction layer that securely manages communication between clients and microservices via API. Also known as an API Gateway, API middleware or in some cases Service Mesh.
Kong acts as the service registry, keeping a record of the available target instances for the upstream services. When a target comes online, it must register itself with Kong by sending a request to the Admin API. Each upstream service has its own ring balancer to distribute requests to the available targets.
With client-side discovery, the client or API gateway making the request is responsible for identifying the location of the service instance and routing the request to it. The client begins by querying the service registry to identify the location of the available instances of the service and then determines which instance to use. See https://konghq.com/learning-center/microservices/service-discovery-in-a-microservices-architecture/
Kong uses an external datastore to store its configuration such as registered APIs, Consumers and Plugins. Plugins themselves can store every bit of information they need to be persisted, for example rate-limiting data or Consumer credentials. See https://konghq.com/faqs/#:~:text=PostgreSQL%20is%20an%20established%20SQL%20database%20for%20use,Cassandra%20or%20PostgreSQL%2C%20Kong%20maintains%20its%20own%20cache.