UAV Path Prediction(v0.1)
Introduction
We utilize collected data from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) movements in the x, y, and z axes as input for model training. The Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) architecture is employed to train the model, and the OSC AIMLFW framework is used as the training model framework. Through this process, a model capable of predicting the path of UAVs is trained, providing a solution for various use cases.
Ensure that the Influx database is operational for this use case, which is based on the OSC AI/ML Framework (Release-H).
Getting Started (Start from data insertion)
- Step 1. Query influx token
- Step 2. Create “UAVData” bucket (Inside Influx DB container)
- Step 3. Fill the file config (UAV_insert.py)
- Step 4. Excute the insert processing to insert data into Influx DB
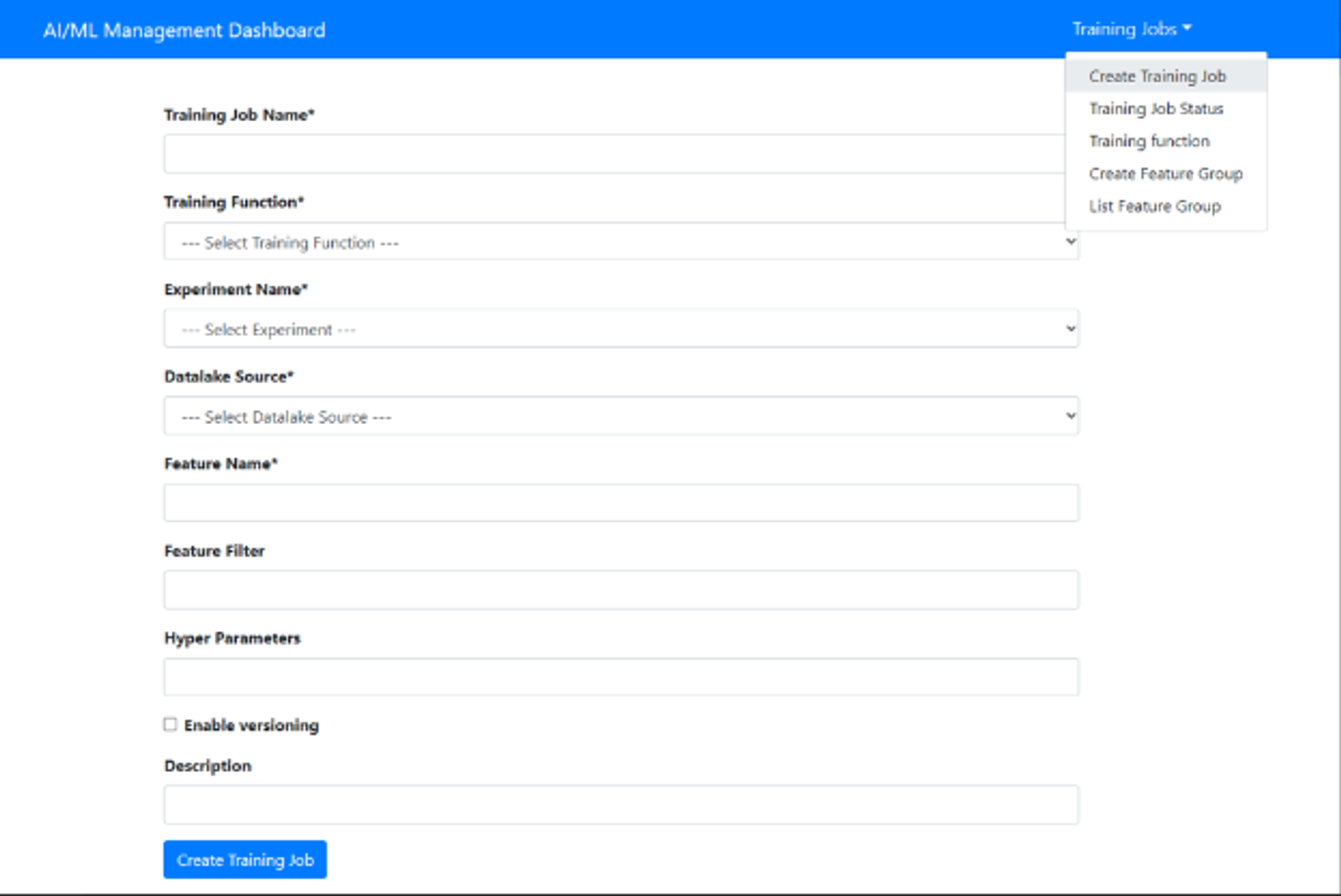
- Step 5. Upload UAV_pipeline.ipynb to aiml-notebook and generate a UAV_pipeline.yaml
- Step 6. Start a UAV model training job
- Step 7. Load the UAV model
(To be added...)
- Step 1. Query influx token
File List
UAV_dataset.csv (Download)
The file contains collected UAV movement path data.UAV_insert.py (Download)
The file processes the UAV_dataset and inserts the data into InfluxDB.
(Changed required: DATASET_PATH , INFLUX_IP , INFLUX_TOKEN)UAV_pipeline.ipynb (Download)
The file defines the model structure and training process.UAV_input.json (Unfinished)
The json file is used for sample data.UAV_predict.sh (Unfinished)
The script used for excuting the model prediction.
Prediction
Input:
This input data represents a collection of points in a three-dimensional space, with each point defined by a set of three coordinates corresponding to the x, y, and z axes (After normalization).Output:
The output should be next xyz-axis path prediction (After normalization).